Webpack: Simplifying Asset Management for Atlassian Plugins
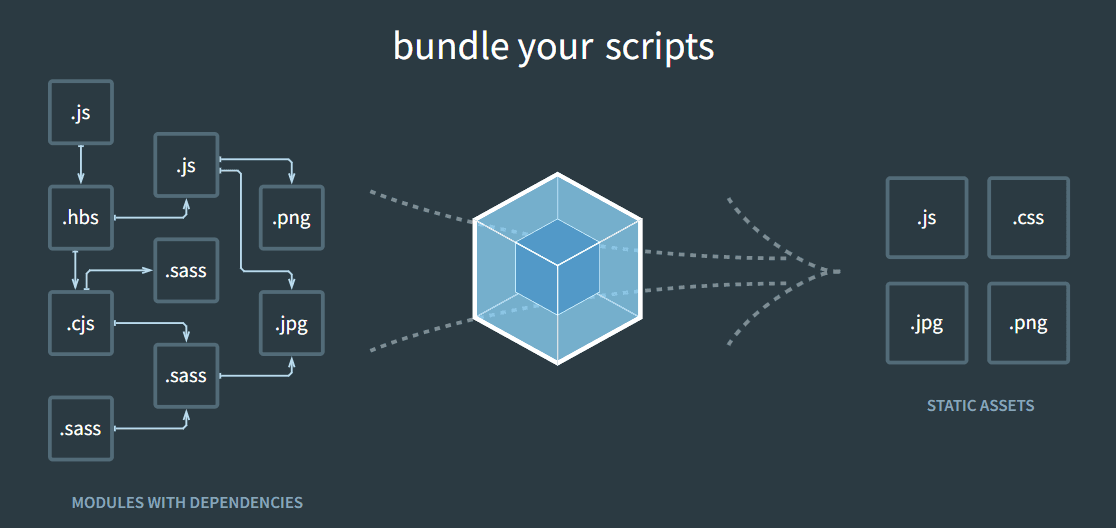
Understanding Webpack
Webpack serves as a crucial tool for bundling various pieces of code and resources required for a website or application to function seamlessly. It acts as a packing machine, efficiently organizing and optimizing assets like JavaScript files, CSS stylesheets, images, and fonts, thereby enhancing performance and usability.
Why Webpack in Atlassian Workflows
Atlassian's suite of products, including Jira, Confluence, and Bitbucket, often rely on plugins to extend their functionalities. Efficient plugin development, testing, and maintenance are crucial for seamless integration. Webpack plays a pivotal role in streamlining these workflows by automating tasks, optimizing assets, and promoting modular code structures.
Advantages of Webpack for Atlassian Plugin Development
Ease of Configuration: Webpack offers extensive configuration options, allowing developers to tailor build processes to specific project requirements. While this flexibility offers versatility, it may present a learning curve for beginners.
Performance Optimization: Webpack's optimization features, such as code splitting, tree shaking, and caching, significantly enhance performance by reducing bundle sizes and loading times. This ensures efficient resource utilization within Atlassian plugins.
Vibrant Community and Ecosystem: With a robust community and vast ecosystem of plugins and loaders, Webpack provides comprehensive support and resources for developers. This active ecosystem facilitates seamless integration and enhances productivity.
Bundle Size Reduction: By leveraging Webpack's advanced optimization techniques, developers can effectively minimize bundle sizes, resulting in faster loading times and improved user experiences.
Enhanced Development Experience: Webpack offers features like Hot Module Replacement (HMR) and built-in development servers, enabling real-time feedback and rapid iteration cycles. This fosters a conducive environment for efficient plugin development.
Comparing Webpack with Alternatives
While Webpack is a popular choice for Atlassian plugin development, alternatives like Parcel and Rollup offer distinct advantages:
Parcel emphasizes zero-configuration setups and optimal bundle sizes out of the box, catering to developers seeking simplicity and convenience.
Rollup focuses on producing highly optimized bundles, making it ideal for performance-critical projects such as libraries and frameworks.
Code Structure for Plugin Development with Webpack
Organizing Atlassian plugin projects with Webpack typically involves separating backend and frontend components:
Backend: Contains Java source code files, resources, and test code, along with Maven project configuration (pom.xml).
Frontend: Houses frontend source files, including components, pages, stylesheets, and entry points (index.js). This directory also includes public assets and configuration files like package.json and webpack.config.js.

Challenges and Solutions
While Webpack offers numerous benefits, developers may encounter challenges such as complex configuration, slow build processes, version compatibility issues, and debugging difficulties. Solutions include leveraging configuration tools, optimizing build processes, maintaining consistent dependencies, and utilizing source maps for debugging.
Integrating Webpack with Atlassian Projects
Integrating Webpack into Atlassian projects involves setting up, configuring, and bundling assets using webpack.config.js. Developers can then deploy bundled files into the appropriate plugin directories and test changes using Webpack's development server.
1. Setup Webpack: Begin by installing Webpack and related dependencies in your project using npm or yarn:npm install --save-dev webpack webpack-cli
2. Configure Webpack: Add this plugin to your webpack config. For every entry point webpack generates, an appropriate <web-resource> definition will be generated in an XML file for you, which can then be bundled in to your Atlassian product or plugin, ready to be served to the browser at product runtime.
const WrmPlugin = require('atlassian-webresource-webpack-plugin');
module.exports = {
entry: {
'my-feature': path.join(FRONTEND_SRC_DIR, 'simple.js')
},
plugins: [
new WrmPlugin({
pluginKey: 'my.full.plugin.artifact-id',
contextMap: {
'my-feature': ['atl.general']
},
xmlDescriptors: path.resolve(OUTPUT_DIR, 'META-INF', 'plugin-descriptors', 'wr-defs.xml')
}),
],
output: {
filename: 'bundled.[name].js',
path: path.resolve(OUTPUT_DIR)
}
};
The output will go to <OUTPUT_DIR>/META-INF/plugin-descriptors/wr-defs.xml, and look something like this:
<bundles>
<web-resource key="entrypoint-my-feature">
<transformation extension="js">
<transformer key="jsI18n"/>
</transformation>
<context>atl.general</context>
<resource name="bundled.my-feature.js" type="download" location="bundled.my-feature.js" />
</web-resource>
</bundles>
In your plugin project's pom.xml file, add the META-INF/plugin-descriptors directory as a value to an <Atlassian-Scan-Folders> tag in the <instruction> section of the AMPS plugin's build configuration.
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<!-- START of a bunch of stuff that is probably different for your plugin, but is outside
the scope of this demonstration -->
<groupId>com.atlassian.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-amps-plugin</artifactId>
<version>6.2.11</version>
<!-- END differences with your plugin -->
<configuration>
<instructions>
<Atlassian-Scan-Folders>META-INF/plugin-descriptors</Atlassian-Scan-Folders>
</instructions>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>Develop and Bundle: Write your plugin code, and use Webpack to bundle your assets.
npx webpack --config webpack.config.js
Integrate with Atlassian: Deploy the bundled files into the appropriate Atlassian plugin directories and configure the plugin manifest to include the new assets.
Test and Iterate: Use Webpack’s development server to test changes in real-time, making the development process faster and more efficient.
Conclusion
By harnessing Webpack's capabilities, developers can streamline Atlassian plugin development, optimize asset management, and enhance overall productivity. Despite challenges, Webpack remains a valuable asset in the developer toolkit, offering powerful features and extensive customization options for building robust, high-performance plugins.
References
Watch this AtlasCamp 2018 talk which uses this plugin amongst others to make your devloop super fast: https://youtu.be/VamdjcJCc0Y
Watch this AtlasCamp 2017 talk about how to build and integrate your own front-end devtooling on top of P2, which introduced the alpha version of this plugin: https://youtu.be/2yf-TzKerVQ?t=537